 Reference: http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/2250_Mutagenesis.html
Reference: http://www.mun.ca/biology/scarr/2250_Mutagenesis.htmlNonsense Mutations- the term "nonsense mutation is used because the stop codon has "no sense" for an amino acid. Nonsense mutations cause the protein to be cut off early and therefore incomplete, which usually renders it non-functional. Cystic fibrosis is a disease caused by a nonsense mutation.
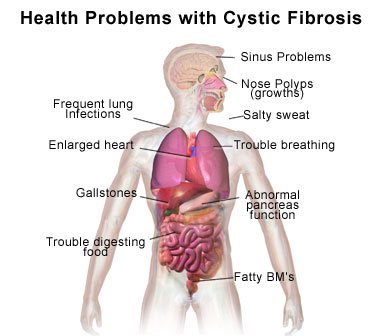 Reference: http://www.drugs.com/cg/cystic-fibrosis.html
Reference: http://www.drugs.com/cg/cystic-fibrosis.htmlDeletion mutation- a type of gene mutation wherein the deletion (as well as addition) of a number of nucleotides cuases a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, which may eventually lead to the alteration in the amino acid sequence at protein translation.

Reference: http://www.intelihealth.com/IH/ihtIH/WSIHW000/32193/32195/353894.html?d=dmtGenetics_BasicContent
Insertion Mutation- a type of mutation resulting from the addition of extra nucleotides in a DNA sequence or chromosome.
Frameshift mutation- a type of gene mutation wherein the addition or deletion of a number of nucleotides causes a shift in the reading frame of the codons in the mRNA, which may lead to a change in the amino acid sequence in protein translation.

Point mutation - the simplest kind of genetic mutation, which can cause dramatic effects to arise from such a small substitution in the genome.

Translocation mutation- this happens when on of two homologous chromosomes breaks and binds to the other. Usually this sort of mutation is very dangerous.


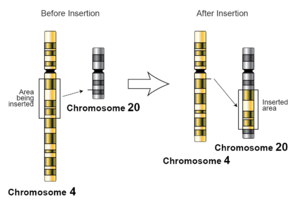 Reference:
Reference:
No comments:
Post a Comment